实验2 SQL 查询语句
2.1 单表查询
2.1.1 实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握SQL查询语句的基本概念。
(2) 掌握SQL Server查询语句的基本语法。
(3) 熟练使用SQL的SELECT语句对单表进行查询。
(4) 熟练掌握并运用SQL Server所提供的函数。
(5) 熟练使用SQL语句进行单表聚合操作。
2.1.2 实验内容
在订单数据库OrderDB中,完成如下的查询:
(1) 查询名字中含有“有限”的客户名称和所在地。
(2) 查询出姓“张”并且姓名的最后一个字为“梅”的员工。
(3) 查询住址中含有“上海”或“南昌”的女员工,并显示其姓名、所属部门、职务、住址、出生日期和性别,其中如果出生日期为空,显示“不详”,否则按格式“yyyy-mm-dd”显示,性别用“男”和“女”显示。
(4) 选取编号不在C20150001~C20150004之间的客户编号、客户名称、客户地址。
(5) 在订单主表中选取订单金额最高的前10%的订单数据。
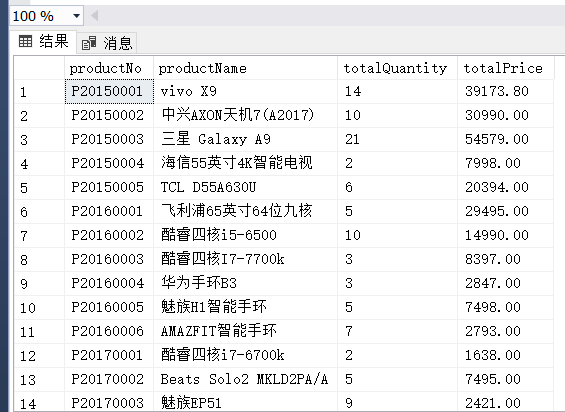
(6) 计算出一共销售了几种商品。
(7) 计算OrderDetail表中每种商品的销售数量、平均销售单价和总销售金额,并且依据销售金额由大到小排序输出。
(8) 按客户编号统计每个客户2015年3月的订单总金额。
(9) 统计至少销售了10件以上的商品编号和销售数量。
(10) 统计在业务科工作且在1987年或1988年出生的员工人数和平均工资。
2.1.3 SQL语句
(1)
select customerName,address
from Customer
where customerName like '%有限%'(2)
select employeeName
from Employee
where employeeName like '张_梅' or employeeName like '张__梅'(3)
select employeeName,department,headShip,address,
case birthday when null then '不详'
else FORMAT(birthday,'yyyy-MM-dd')
end as birthday,
性别 = case sex when 'M' then '男'
when 'F' then '女'
end
from Employee
where address like '%南昌%' or employeeName like '%上海%'(4)
select customerNo,customerName,address
from Customer
where customerNo not between 'C20150001' and 'C20150004'(5)
update OrderMaster set orderSum=sum2
from OrderMaster a,(select
orderNo,sum(quantity*price) sum2
from OrderDetail
group by orderNo) b
where a.orderNo=b.orderNo
select top 10 percent
orderNo,customerNo,salerNo,orderDate,orderSum,invoiceNo
from OrderMaster
order by orderSum desc(6)
select count(distinct productNo) as TotalProductCount
from OrderDetail;(7)
select
productNo,
sum(quantity) as totalQuantity,
avg(price) as averagePrice,
sum(quantity * price) as totalAmount
from OrderDetail
group by productNo
order by totalAmount desc;(8)
select
customerNo,
sum(orderSum) as totalorderSum
from OrderMaster
where year(orderDate) = 2015 and month(orderDate) = 3
group by customerNo(9)
select
productNo,
sum(quantity) as totalquantity
from OrderDetail
group by productNo
having sum(quantity) >= 10(10)
select
count(*) as employeeCount,
avg(salary) as avgsalary
from Employee
where department = '业务科' and (year(birthday) = 1987 or year(birthday) = 1988)2.1.4 运行结果
(1)
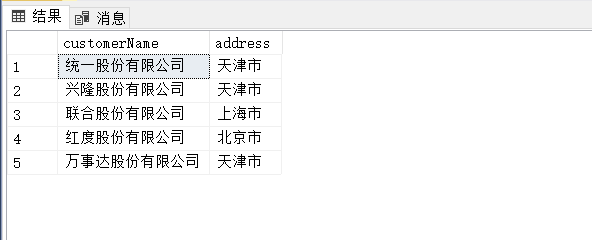
(2)
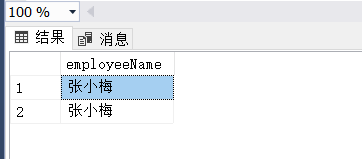
(3)
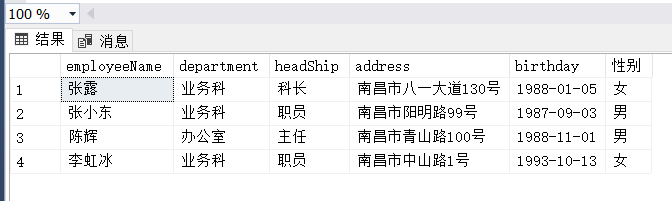
(4)
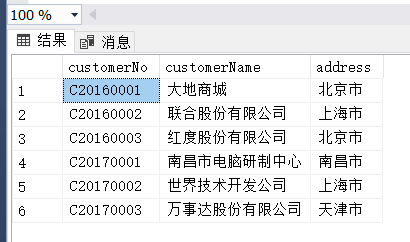
(5)
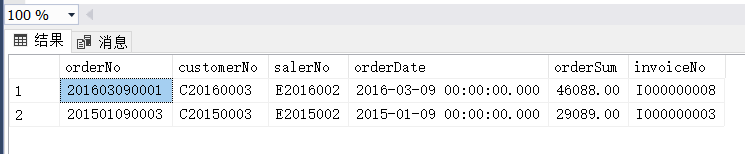
(6)
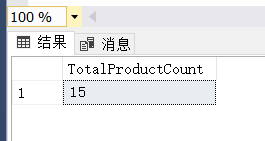
(7)
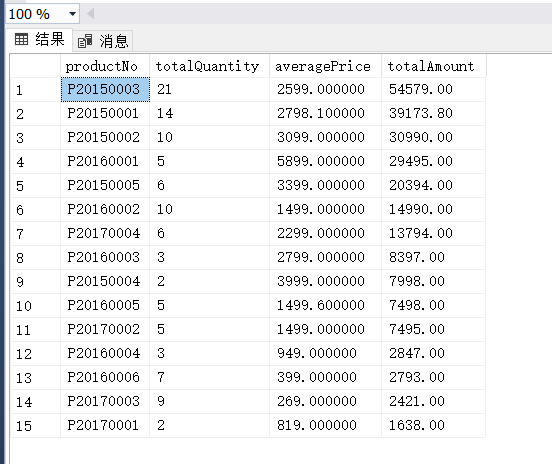
(8)
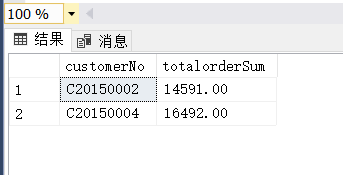
(9)
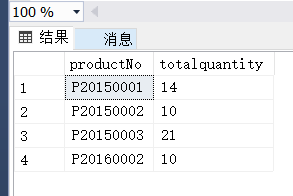
(10)
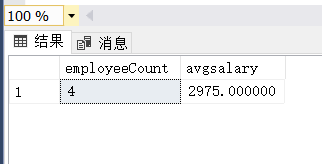
2.2 多表查询
2.2.1 实验目的与要求
(1) 熟练掌握SQL语句的使用。
(2) 熟练使用SQL语句进行连接操作。
2.2.2 实验内容
在订单数据库OrderDB中,完成如下的查询:
(1) 找出同一天进入公司服务的员工。
(2) 在Employee表中查询薪水超过员工平均薪水的员工信息。
(3) 查询没有订购商品的客户编号和客户名称。
(4) 使用子查询查找“酷睿四核I7-7700k”的销售情况,要求显示相应的销售员的姓名、性别,销售日期、销售数量和金额,其中性别用“男”、“女”表示。
(5) 查找每个员工的销售记录,要求显示销售员的编号、姓名、性别、商品名称、数量、单价、金额和销售日期,其中性别使用“男”和“女”表示,日期使用“yyyy-mm-dd”格式显示。
(6) 分别使用左外连接、右外连接、完整外部连接查询单价高于400元的商品编号、商品名称、订货数量和订货单价,并分析比较检索的结果。
(7) 查询单价高于400元的商品编号、商品名称、订货总数量和订货总价。
(8) 查询OrderMaster表中订单金额最高的订单号及订单金额。
(9) 查找订购总金额在5000元以上的客户编号、客户名称和订购总金额。
(10) 查询每种商品的总销售数量及总销售金额,要求显示出商品编号、商品名称、总数量及总金额,并按商品号从小到大排列。
2.2.3 SQL语句
(1)
select *
from Employee
where convert(date, hireDate) IN (
select convert(date, hireDate)
from Employee
group by convert(date, hireDate)
having count(*) > 1
)
order by hireDate;(2)
select *
from Employee
where salary > (
select avg(salary)
from Employee)(3)
select customerNo,customerName
from Customer
where customerNo not in(
select customerNo
from OrderMaster
)(4)
select a.employeeName,
性别 = case a.sex when 'M' then '男'
when 'F' then '女'
end, b.orderDate, c.quantity,
金额 = c.quantity*c.price
from Employee a, OrderMaster b, OrderDetail c
where a.employeeNo=b.salerNo and b.orderNo=c.orderNo and
c.productNo=d.productNo and productName='酷睿四核I7-7700k'
order by a.employeeNo(5)
select a.employeeNo,a.employeeName,
性别 = case a.sex when 'M' then '男'
when 'F' then '女'
end, d.productName,c.quantity,c.price,
金额 = c.price*c.quantity,
销售日期 = case b.orderDate when null then '不详'
else FORMAT(b.orderDate,'yyyy-MM-dd')
end
from Employee a, OrderMaster b, OrderDetail c, Product d
where a.employeeNo=b.salerNo and b.orderNo=c.orderNo and
c.productNo=d.productNo(6)
左外连接:
SELECT p.productNo, p.productName, od.quantity, od.price
FROM Product p
LEFT JOIN OrderDetail od ON p.productNo = od.productNo
WHERE p.productPrice > 400右外连接:
SELECT p.productNo, p.productName, od.quantity, od.price
FROM OrderDetail od
RIGHT JOIN Product p ON od.productNo = p.productNo
WHERE p.productPrice > 400全外连接:
SELECT p.productNo, p.productName, od.quantity, od.price
FROM OrderDetail od
FULL OUTER JOIN Product p ON od.productNo = p.productNo
WHERE p.productPrice > 400(7)
SELECT p.productNo, p.productName, SUM(od.quantity) AS totalQuantity, SUM(od.price * od.quantity) AS totalPrice
FROM Product p
JOIN OrderDetail od ON p.productNo = od.productNo
WHERE p.productPrice > 400
GROUP BY p.productNo, p.productName(8)
select top 1 a.orderNo,sum(b.price * b.quantity) as totalPrice
from OrderMaster a
join OrderDetail b on a.orderNo = b.orderNo
group by a.orderNo
order by totalPrice desc(9)
select a.customerNo,a.customerName,sum(c.price * c.quantity) as totalPrice
from Customer a,OrderMaster b,OrderDetail c
where a.customerNo = b.customerNo and b.orderNo = c.orderNo
group by a.customerNo,a.customerName
having sum(c.price * c.quantity) >= 5000(10)
select d.productNo,d.productName,sum(c.quantity) as totalQuantity,sum(c.price * c.quantity) as totalPrice
from OrderMaster b,OrderDetail c,Product d
where d.productNo = c.productNo and b.orderNo = c.orderNo
group by d.productNo,d.productName
order by productNo2.2.4 运行结果
(1)
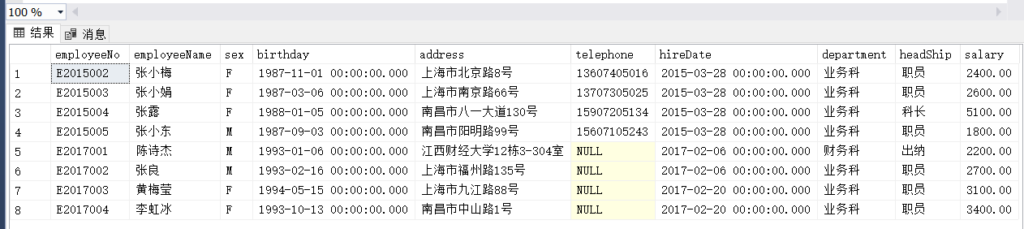
(2)
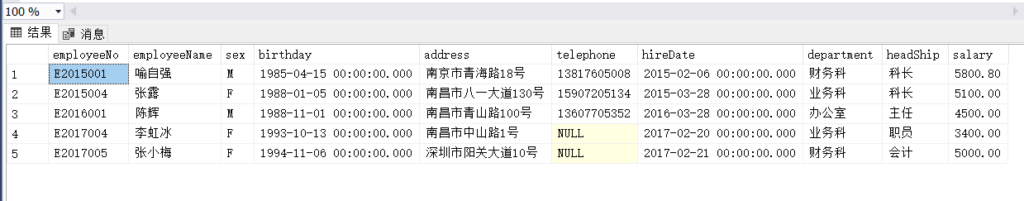
(3)

(4)
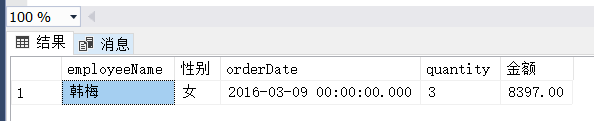
(5)
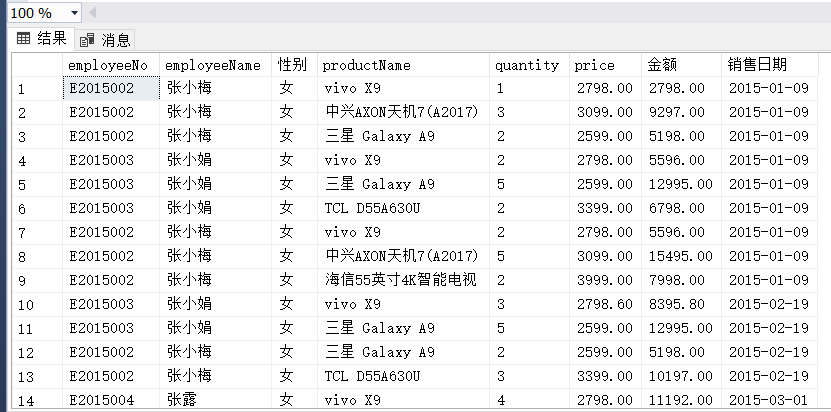
(6)
左外连接:
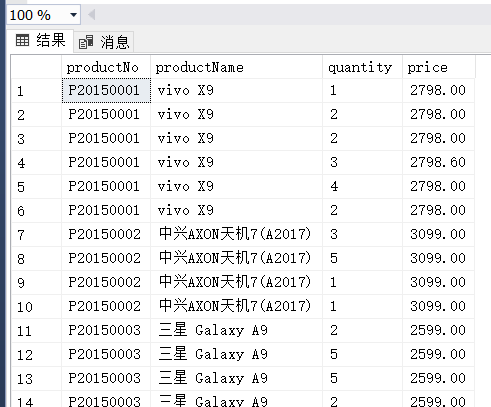
右外连接:
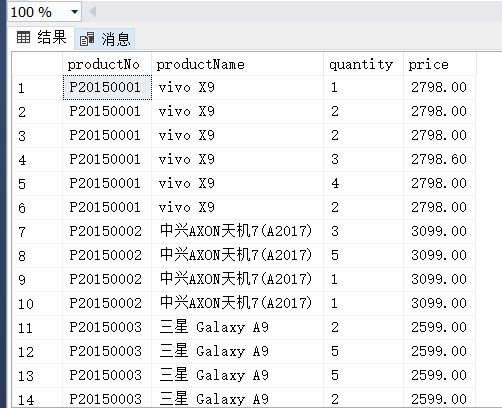
全外连接:
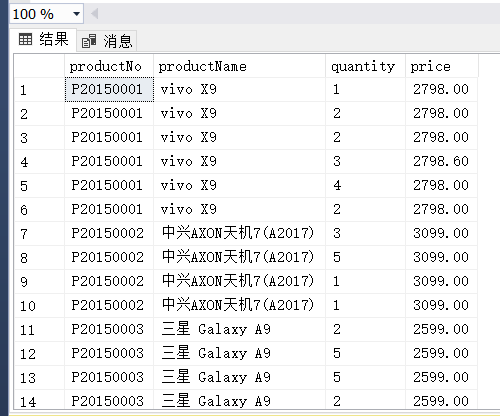
(7)
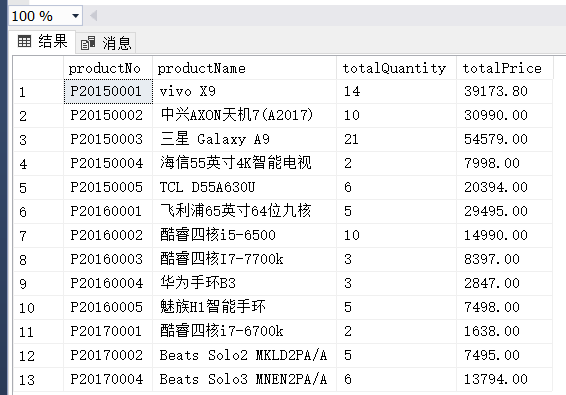
(8)
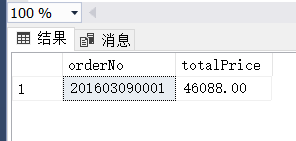
(9)
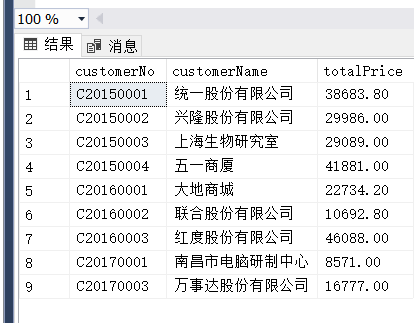
(10)
2.3 复杂查询
2.3.1 实验目的与要求
(1) 熟练掌握存在量词(选学)、查询表的使用方法。
(2) 熟练使用SQL语句进行复杂的数据汇总操作。
2.3.2 实验内容
在订单数据库OrderDB中,完成如下的查询:
(1) 在订单明细表中查询订单金额最高的订单。
(2) 找出至少被订购3次的商品编号、订单编号、订货数量和订货金额,并按订货数量的降序排序输出。
(3) 查询订购的商品数量没有超过10个的客户编号和客户名称。
(4) 查找至少订购了3种商品的客户编号、客户名称、商品编号、商品名称、数量和金额。
(5) 查询单笔销售金额最高的销售员编号及其所有订单编号、订单日期和订单金额。
(6) 求每位客户订购的每种商品的总数量及平均单价,并按客户号、商品号从小到大排列。
(7) 查询业绩最好的业务员号、业务员名及其总销售金额。
(8) 用存在量词查找没有订货记录的客户名称(选做)。
(9) 查询至少包含了“手环”这类商品的订单的订单号、客户名称、商品名称、数量和单价。
(10) 查询既订购了“酷睿四核”商品,又订购了“华为手环”商品的客户编号、订单编号和订单金额。
2.3.3 SQL语句
(1)
select top 1 a.orderNo,sum(a.price * a.quantity) as totalPrice
from OrderDetail a
group by a.orderNo
order by totalPrice desc(2)
select d.productNo,c.orderNo,sum(c.quantity) as totalquantity,sum(c.quantity*c.price) as totalprice
from OrderDetail c,Product d
group by d.productNo,c.orderNo,c.quantity
having sum(c.quantity)>=3
order by totalquantity desc(3)
select a.customerNo,a.customerName
from Customer a,OrderDetail b,OrderMaster c
where a.customerNo = c.customerNo and b.orderNo = c.orderNo
group by a.customerNo,a.customerName
having sum(b.quantity) <= 10(4)
select a.customerNo,a.customerName,d.productNo,d.productName,b.quantity,sum(b.price * b.quantity) as totalPrice
from Customer a,OrderDetail b,OrderMaster c,Product d
where a.customerNo = c.customerNo and b.orderNo = c.orderNo and b.productNo = d.productNo
group by a.customerNo,a.customerName,d.productNo,d.productName,b.quantity,b.price
having sum(b.quantity) >= 3(5)
select top 1 om.salerNo,om.orderNo,om.orderDate,om.orderSum
from OrderMaster om
inner join (
select salerNo, max(orderSum) as maxSum
from OrderMaster
group by salerNo
) t on om.salerNo = t.salerNo and om.orderSum = t.maxSum
order by om.orderSum desc(6)
select c.customerNo,p.productNo,sum(od.quantity) as totalquantity,od.price
from OrderMaster om,Product p,OrderDetail od,Customer c
where om.orderNo = od.orderNo and c.customerNo = om.customerNo and p.productNo = od.productNo
group by c.customerNo,p.productNo,od.price
order by c.customerNo(7)
select top 1 a.employeeNo,a.employeeName,sum(c.price*c.quantity) as totalprice
from Employee a, OrderMaster b, OrderDetail c, Product d
where a.employeeNo=b.salerNo and b.orderNo=c.orderNo and
c.productNo=d.productNo
group by a.employeeNo,a.employeeName
order by totalprice desc(8)
存在量词选学,跳过
(9)
select om.orderNo, c.customerName, p.productName, od.quantity, od.price
from OrderMaster om,Customer c,OrderDetail od,Product p
where p.productName like '%手环%' and od.productNo = p.productNo and om.orderNo = od.orderNo and om.customerNo = c.customerNo(10)
select c.customerNo,om.orderNo, sum(od.quantity*od.price) as orderSum
from OrderMaster om,Customer c,OrderDetail od , (select * from Product where productName like '%酷睿四核%')p1
, (select * from Product where productName like '%华为手环%')p2
where om.orderNo = od.orderNo and om.customerNo = c.customerNo
and p1.productNo = od.productNo and od.productNo = p2.productNo
group by c.customerNo,om.orderNo
2.3.4 运行结果
(1)
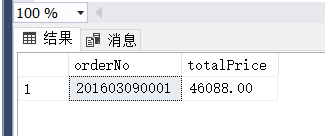
(2)
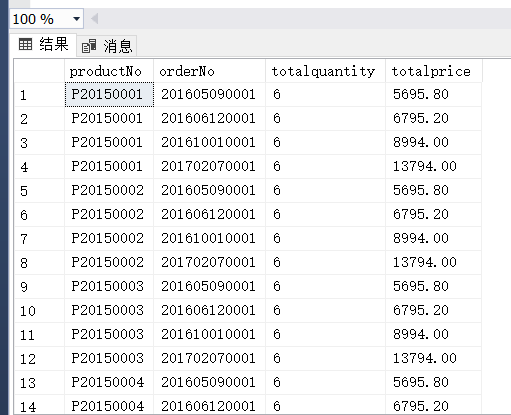
(3)
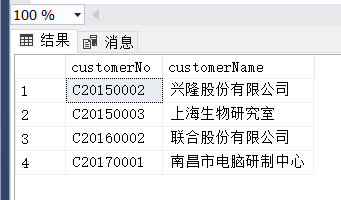
(4)
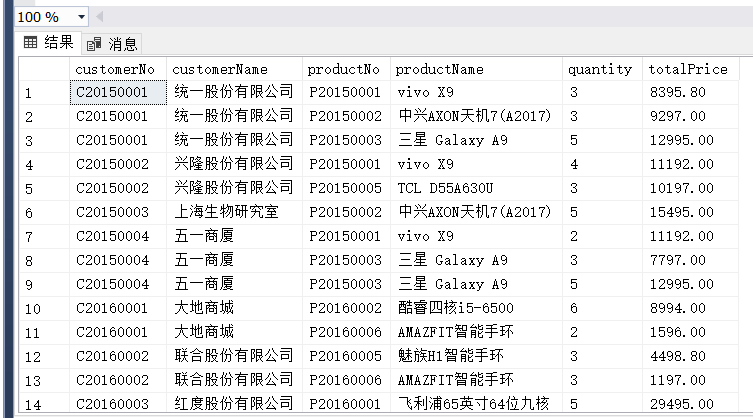
(5)
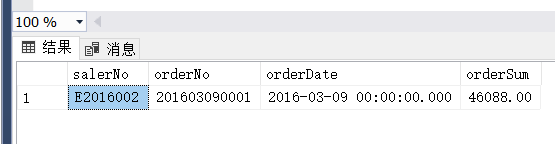
(6)
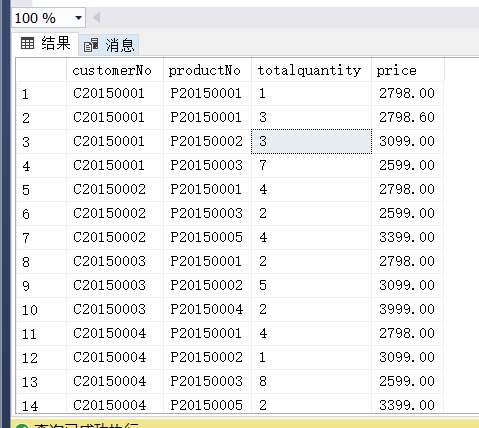
(7)
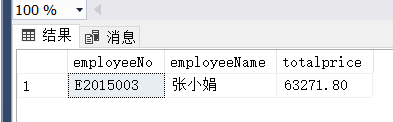
(8)
存在量词选学,跳过
(9)
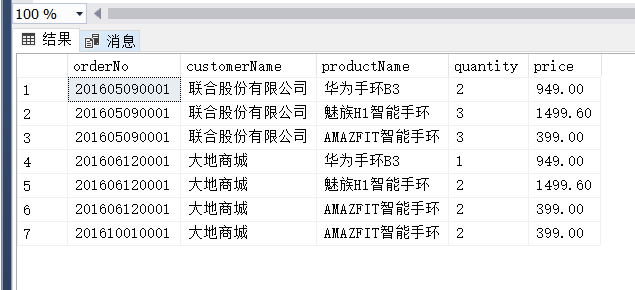
(10)
2.4. 总结
本次实验让我进一步了解了SQL的查询语句,即单表查询,多表查询,复杂查询,为以后更好地学习SQL打下了坚实基础。
参考文献
[1] 数据库系统原理与设计(第三版) 万常选、廖国琼、吴京慧、刘喜平编著
[2] JOIN与INNER JOIN区别 .CSDN博主「豆虫儿」








Comments NOTHING