1、专题名称
回溯算法的设计与分析
2、实践内容
2.1 实践内容 1
(1)题目要求
幂集。编写一种方法,返回某集合的所有子集。集合中不包含重复的元素。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
-
示例:
输入: nums = [1,2,3] 输出: [ [3], [1], [2], [1,2,3], [1,3], [2,3], [1,2], [] ]
(2)算法设计
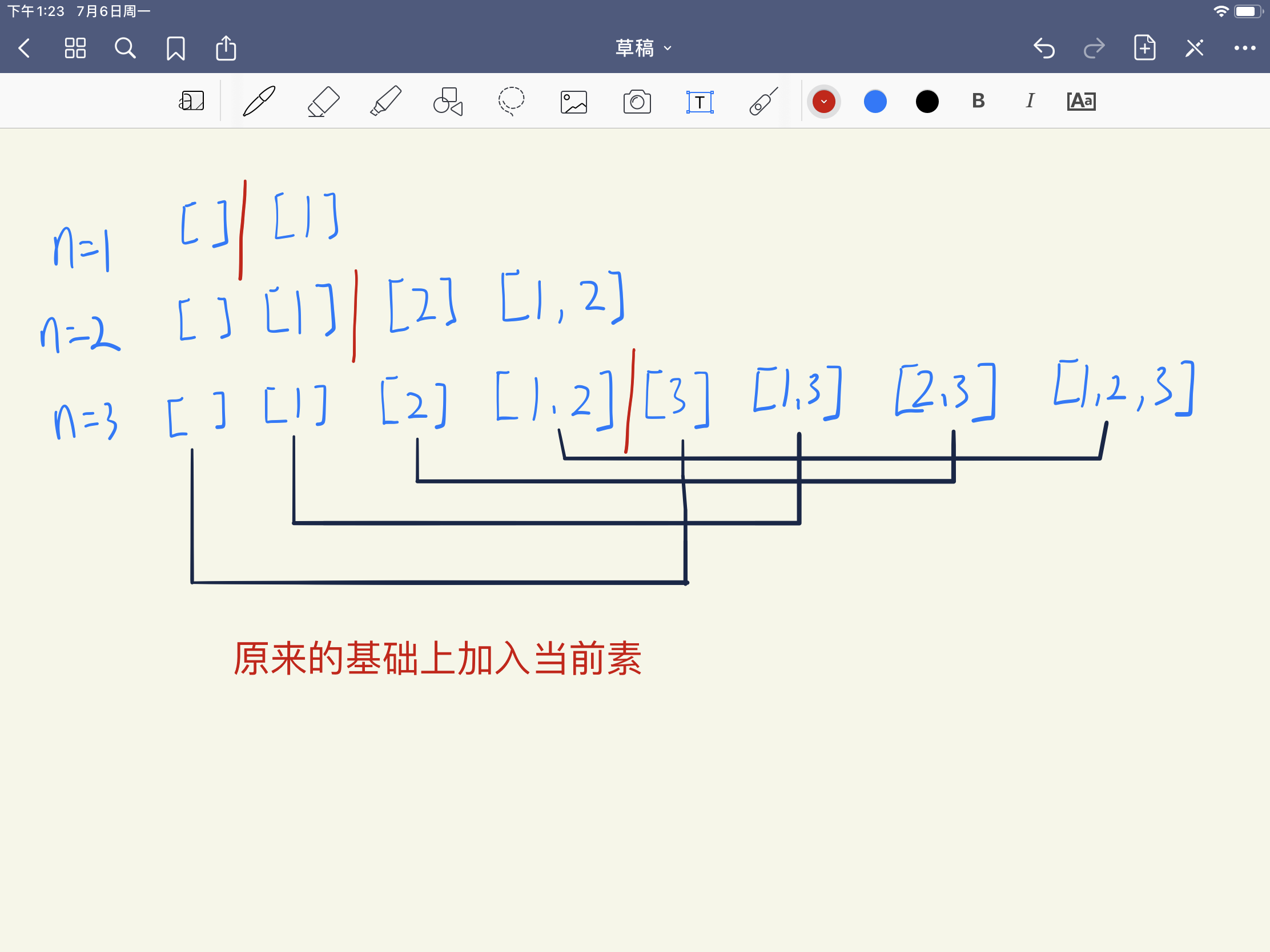
(3)代码实现
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int>>ans;
ans.push_back({}); // 默认有个空子集
for(auto p : nums)
{
int n = ans.size(); // 在原有集合的基础上,取出每个集合加上当前元素,然后再加入到集合中
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
{
vector<int>temp = ans[i];
temp.push_back(p);
ans.push_back(temp);
}
}
return ans;
}
};(4)算法分析
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
算法优点:时间复杂度和空间复杂度都低。
缺点:要把题目转换为数学问题来解决
2.2 实践内容 2
(1)题目要求
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n × n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回 n 皇后问题 不同的解决方案的数量。
示例 1:
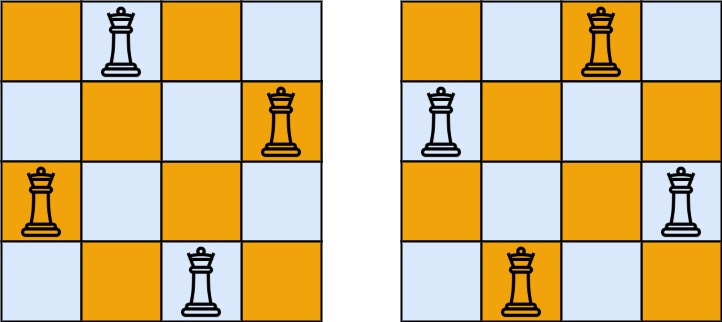
输入:n = 4
输出:2
解释:如上图所示,4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。示例 2:
输入:n = 1
输出:1 提示:
1 <= n <= 9
(2)算法设计
使用递归遍历每一行,用vector
(3)代码实现
lass Solution {
public:
//递归:遍历每一行,用vector<int> n保存行为i 时的皇后在j列,不能放在斜边:即新的x - y != 已经存在的i - j || (x + y != i + j)
vector<int> v;
unordered_map<int, int> m; //保存用过的列
int ans = 0;
void dfs(int row, int n) {
if (row > n) {
ans++;
return;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { //row行的列
if (m.find(j) == m.end()) {
int condition = 1;
for (int k = 1; k < row; k++) {
if (k - v[k] == row - j || k + v[k] == row + j) { //验证对角线是否满足条件
condition = 0;
break;
}
}
if (condition == 1) {
v[row] = j;
m[j]++;
dfs(row + 1, n);
v[row] = 0; // 回溯
m.erase(j); // 删除key为j的map?
}
}
}
}
int totalNQueens(int n) {
v.resize(n + 5);
dfs(1, n);
return ans;
}
//time : n*n* 不过时间复杂度好像不会算...........
//space : n 疑惑这个哈希表的空间复杂度?
};(4)算法分析
时间复杂度:O(n^2)
空间复杂度:O(n)
算法优点:空间复杂度低,时间复杂度较低。
缺点:非常难想
2.3 实践内容 3
(1)题目要求
-
- 给定一个不含重复数字的数组
nums,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1] 输出:[[0,1],[1,0]]示例 3:
输入:nums = [1] 输出:[[1]]提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 6-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有整数 互不相同
- 给定一个不含重复数字的数组
(2)算法设计
比较常规的回溯问题,对特殊情况进行了特殊处理
(3)代码实现
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> total;
void dfs(int now,int sum,vector<int> &past,vector<int> &push,vector<int> &nums){
for(int i = 0 ; i < sum ; i++){
int flag = 0;
if(now == 1 && sum == 1){ // 对只有一个元素的特殊情况
past.push_back(i);
push.push_back(nums[i]);
total.push_back(push);
break;
}
else{
for(int j = 0 ; j < past.size() ; j++){
if(i == past[j])
flag = 1;
}
if(flag)
continue;
}
if(now == sum){ // 数组内元素足够
past.push_back(i);
push.push_back(nums[i]);
total.push_back(push);
}
else{
past.push_back(i);
push.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(now+1,sum,past,push,nums);
}
if(past.size())
past.pop_back(); // 删减元素
if(push.size())
push.pop_back(); // 删减元素
}
}
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {
int sum = nums.size(),totalnum = 1;
vector<int> past;
vector<int> push;
dfs(1,sum,past,push,nums);
return total;
}
};(4)算法分析
时间复杂度:O(n!)
空间复杂度:O(n)
算法优点:稍微易想。
缺点:要对C++的容器有一定的了解。
2.4 实践内容 4
(1)题目要求
-
二进制手表顶部有 4 个 LED 代表 小时(0-11),底部的 6 个 LED 代表 分钟(0-59)。每个 LED 代表一个 0 或 1,最低位在右侧。
- 例如,下面的二进制手表读取
"4:51"。
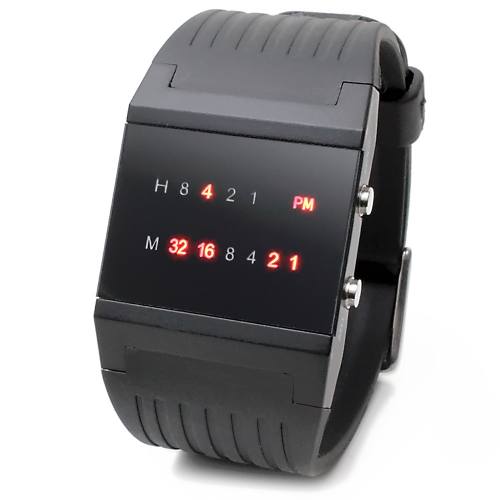

给你一个整数
turnedOn,表示当前亮着的 LED 的数量,返回二进制手表可以表示的所有可能时间。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。小时不会以零开头:
- 例如,
"01:00"是无效的时间,正确的写法应该是"1:00"。
分钟必须由两位数组成,可能会以零开头:
- 例如,
"10:2"是无效的时间,正确的写法应该是"10:02"。
示例 1:
输入:turnedOn = 1 输出:["0:01","0:02","0:04","0:08","0:16","0:32","1:00","2:00","4:00","8:00"]示例 2:
输入:turnedOn = 9 输出:[]提示:
0 <= turnedOn <= 10
- 例如,下面的二进制手表读取
(2)算法设计
比较简单的回溯问题,对特殊情况进行处理,用记忆化搜索思想解决
(3)代码实现
class Solution {
public:
int a[10]={1,2,4,8,1,2,4,8,16,32};
void dfs(int now,int num,int turnedOn,vector<string> &readBinaryWatch1,bool *b){
for(int j = now ; j <= 9 ; j++){
if(9-j+num < turnedOn || num > turnedOn)
break;
int flag = 0;
b[j] = 1;
int hour = 0;
int minute = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i <= 3 ; i++){
if(b[i])
hour+=a[i];
if(hour >= 12)
flag = 1;
}
for(int i = 4 ; i <= 9 ; i++){
if(b[i])
minute+=a[i];
if(minute >= 60)
flag = 1;
}
if(flag){
b[j] = 0;
dfs(j+1,num,turnedOn,readBinaryWatch1,b);
}
else if(num == turnedOn){
string str;
if(minute < 10)
str = to_string(hour) + ":0" + to_string(minute) ;
else
str = to_string(hour) + ":" + to_string(minute) ;
if(find(readBinaryWatch1.begin(),
readBinaryWatch1.end(),str)==readBinaryWatch1.end())
readBinaryWatch1.push_back(str);
}
else{
dfs(j+1,num+1,turnedOn,readBinaryWatch1,b);
}
b[j] = 0;
}
}
vector<string> readBinaryWatch(int turnedOn) {
bool b[10] = {};
vector<string> readBinaryWatch1;
if(turnedOn == 0){
readBinaryWatch1.push_back("0:00");
return readBinaryWatch1;
}
else{
dfs(0,1,turnedOn,readBinaryWatch1,b);
return readBinaryWatch1;
}
}
};(4)算法分析
时间复杂度:O(n!)
空间复杂度:O(n)
算法优点:简单易想。
缺点:空间复杂度和时间复杂度都一般,且需对C++的容器有较好的理解.
2.5 实践内容 5
(1)题目要求
有效 IP 地址 正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成,且不能含有前导 0),整数之间用 '.' 分隔。
- 例如:
"0.1.2.201"和"192.168.1.1"是 有效 IP 地址,但是"0.011.255.245"、"192.168.1.312"和"192.168@1.1"是 无效 IP 地址。
给定一个只包含数字的字符串 s ,用以表示一个 IP 地址,返回所有可能的有效 IP 地址,这些地址可以通过在 s 中插入 '.' 来形成。你 不能 重新排序或删除 s 中的任何数字。你可以按 任何 顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "25525511135"
输出:["255.255.11.135","255.255.111.35"]示例 2:
输入:s = "0000"
输出:["0.0.0.0"]示例 3:
输入:s = "101023"
输出:["1.0.10.23","1.0.102.3","10.1.0.23","10.10.2.3","101.0.2.3"]提示:
1 <= s.length <= 20s仅由数字组成
(2)算法设计
根据题意,可以把IP地址字符串分为四段,三个小数点,注意特殊情况,三重循环遍历即可
(3)代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void dfs(vector<string> &strsum,string str){
for(int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i++){
string comp = "255";
string s1 = str.substr(0,i-0);
cout << "s1:" + s1 << endl;
cout << "i:" + to_string(i) << endl;
if(s1.length()>1&&s1[0] == '0')
continue;
for(int j = i+1 ; j <= i+3 && j < str.length() ; j++){
string s2 = str.substr(i,j-i);
cout << "s2:" + s2 << endl;
cout << "j:" + to_string(j) << endl;
if(s2.length()>1&&s2[0] == '0')
continue;
for(int k = j+1 ; k <= j+3 && k < str.length() ; k++){
string str2;
string s3 = str.substr(j,k-j);
string s4 = str.substr(k,str.length()-k);
cout << "s3:" + s3 << endl;
cout << "s4:" + s4 << endl;
cout << "k:" + to_string(k) << endl;
if(s1.length()>2 && s1 > comp || s2.length()>2 && s2 > comp || s3.length()>2 && s3 > comp || s4.length()>2 && s4 > comp)
continue;
else if(s1.length()>1&&s1[0] == '0' || s2.length()>1&&s2[0] == '0' ||
s3.length()>1&&s3[0] == '0' || s4.length()>1&&s4[0] == '0')
continue;
else if(s1.length()>3 || s2.length()>3 || s3.length()>3 || s4.length()>3)
continue;
str2 = s1 + "." + s2 + "." + s3 + "." + s4;
strsum.push_back(str2);
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
string s;
cin >> s;
vector<string> strsum;
if(s.length()>12 || s.length()<4);
else
dfs(strsum,s);
for(auto x: strsum)
cout << x << endl;
return 0;
}(4)算法分析
时间复杂度:O(n^3)
空间复杂度:O(n)
算法优点:简单易想。
缺点:空间复杂度和时间复杂度都一般,且需熟悉C++的字符串.
3、问题与总结
问题:以上题目对C++的容器,字符串有较高要求,花了一定时间学习
总结:总体耗时较短,且对C++的容器的使用更加熟练
4、完成情况证明








Comments NOTHING